Why Does The Malaria Disease Persist In The Human Population
Why does the malaria disease persist in the human population. The legend of King Arthur has persisted for nearly fifteen centuries. Some evidence suggests that it is also a cause of poverty and a major hindrance to economic development. Although tropical regions are most affected malarias furthest influence reaches into some.
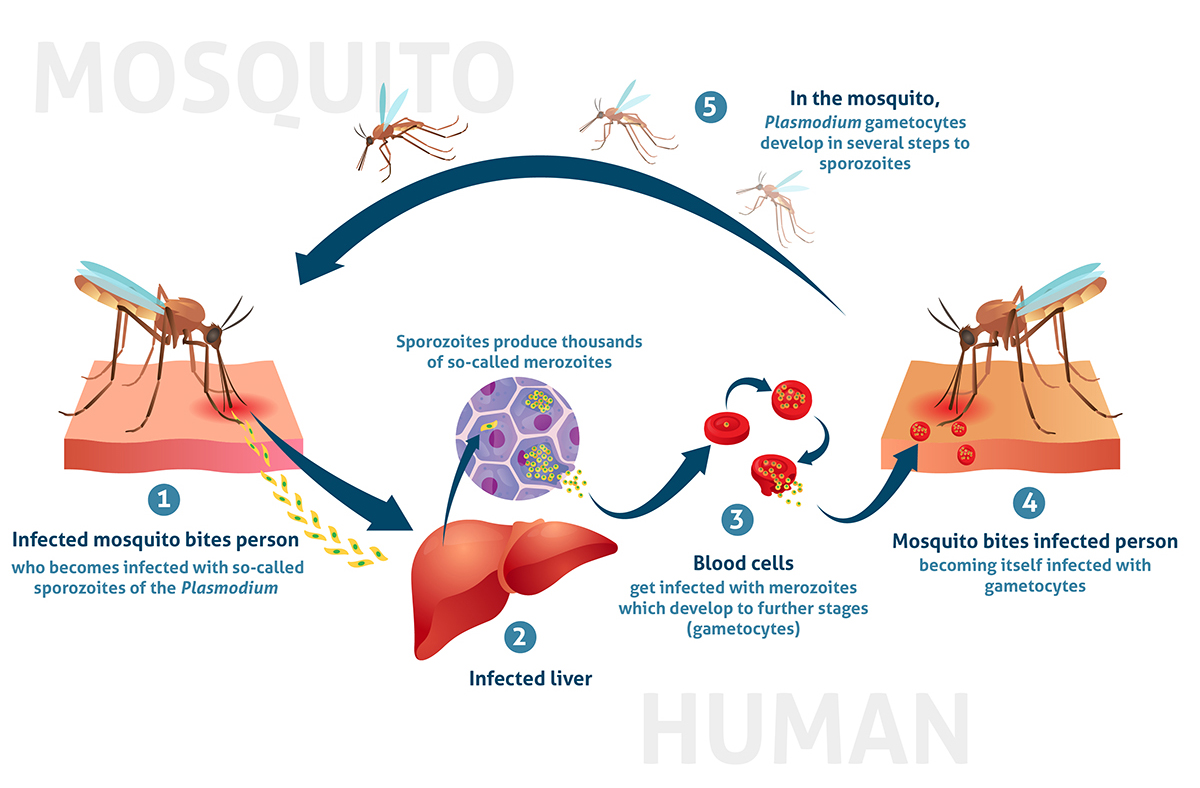
Transmitted through infected mosquitoes the malaria parasite once in the human bloodstream multiplies inside red blood cells which then burst after a few days spreading more infection to other red blood cells and causing severe headache nausea vomiting fever coma and other. Malaria kills roughly 12 million people each year mainly young children in sub-Saharan Africa. Malaria is not just a disease commonly associated with poverty.
During Africas dry season when mosquitoes are scarce malaria parasites have a. However in many parts of the world the gene that causes sickle cell anemia is more common because a single copy of it confers resistance to malaria. Natural selection may not have had time to remove them yet.
The first is that scientists make errors in reporting the genetic causes of a disorder which can occur for any number of. Human migration causes this gene to be found in populations all over the world. In the summer of 1831 an epidemic killed 10 percent of the population of St.
Yet Plasmodium malariae which has no latent forms can persist asymptomatically in the blood for decades and perhaps throughout the entire life of the host 1. People move for a number of reasons including environmental deterioration economic necessity conflicts and natural disasters. These factors are most likely to.
Characteristics of the malaria parasite can influence the occurrence of malaria and its impact on human populations for example. Six major factors account for the discrepancies the researchers write. Occasionally humans can be infected by several simian species like Plasmodium knowlesi recognised as a major cause of human malaria in South-East Asia since 2004.
To persist in working for world peace. Falciparum malaria may progress to severe illness and possibly death.
Plasmodium vivax and Plasmodium ovale are often considered the malaria parasites best adapted to long-term survival in the human host because of their latent exo-erythrocytic forms.
There are a number of possible scenarios. During Africas dry season when mosquitoes are scarce malaria parasites have a. Transmitted through infected mosquitoes the malaria parasite once in the human bloodstream multiplies inside red blood cells which then burst after a few days spreading more infection to other red blood cells and causing severe headache nausea vomiting fever coma and other. Falciparum malaria may progress to severe illness and possibly death. These factors are most likely to. Human migration causes this gene to be found in populations all over the world. To persist in unpopular political activities. Falciparum predominates such as Africa south of the Sahara will suffer more disease and death than areas where other species which tend to cause less severe manifestations predominate. Characteristics of the malaria parasite can influence the occurrence of malaria and its impact on human populations for example.
People move for a number of reasons including environmental deterioration economic necessity conflicts and natural disasters. In the summer of 1831 an epidemic killed 10 percent of the population of St. Today the global malaria situation is serious and. Malaria kills roughly 12 million people each year mainly young children in sub-Saharan Africa. The legend of King Arthur has persisted for nearly fifteen centuries. It turns out that in these areas HbS carriers have been naturally selected because the. There are a number of possible scenarios.

























Posting Komentar untuk "Why Does The Malaria Disease Persist In The Human Population"